 |
|
Reparative cement for endodontic complications.
Composition:
- SiO2 , K20, Al2O3, Na2O, Fe2O3 , SO3, CaO, Bi2O3, MgO.
- Insoluble residues (crystalline silica, calcium oxide and
potassium
sulfate and sodium).
- The main MTA component is calcium oxide, that in contact
with the
humidity of the environment, be converted in calcium
hydroxide. |
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
 |
|
Clincker: is a stone obtained in high temperatures and that
contains
a high concentration of calcareous and argillaceous materials. |
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
 |
|
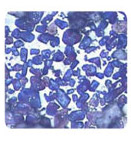
Photomicrography of a clincker: Blue and brownish crystals are
of
alita Interstitial phase is white. |
| |
|
|
| |
|
Indications:
- Treatment of radicular perforations.
- Sealer of external and internal communicating
reabsorptions.
- Retro-obturator material in para-endodontic surgeries.
- Pulp capping in conservative treatments of the pulp.
- Apexification and apexogenesis inductor.
- Material for intracoronary sealing previous to the dental
whitening.
- 95Apical plug for endodontic obturation. |
| |
|
|
| |
|
Advantages:
- Excellent marginal sealer that avoid bacterial migration
and
penetration of tissular fluids to the inside of the root
canal.
- Biological sealing of radicular and furca perforations
through
induction of cement formation.
- Inducing for formation of a dentinal layer when used over
the
pulp.
- Can be use in places with humidity presence, without
losing its
properties. |
| |
|
|
 |
|
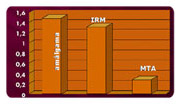
Hydration:
In contact with the water forms a colloidal gel that solidifies,
forming a rigid structure in a period of 10 minutes. MTA has
medium size particles that allows the complete hydration, confirming one of its main advantages, that is, the sealing power.
LEE ET AL - 1993 Average of marginal infiltration in
perforations. |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
Potential of Hydrogenization (pH):
Its pH highly alkaline (12.0) makes the oral environment
inhospitable
for growth of bacteria, maintaining its antibacterial potential
for a long
period.
RELEASING CALCIUM IONS Duarte, M.H. et al. OS.v.95, n.3, p.345,
2003 |
| |
|
|
 |
|
Radiopacity:
White MTA opacity is higher than the dentine and the bone
tissue, and
similar to the of gutta-percha, and for that reason its easy to
visualization in the operative and control x-ray.
Radiopacity of the product is provided by the Bismuth Oxide
compound
and, for showing larger radiopacity than gutta-percha and dentine,
it is
easily identified in x-rays. |
| |
|
|
| |
|
The setting time of MTA is in 10
minutes.
It is not necessary to wait its hardening in order to continue
the
following procedures. One of the important characteristics of
White MTA is
the improvement in its results under moist environment.
In case of extended procedures, the hardening of the cement on
the
plate may take place, and can be difficult to use. For these
situations,
it is recommending to protect it with moist gauze. |
| |
|
|
| |
|
Compression
Resistance:
- Compression resistance after 28 days is 44.2 MPa.
- MTA reveals acceptable compression resistance values,
when
considering that this material is used in regions with no direct
occlusal
load.
Solubility: (between 0.1 and 1%)
- No significant signs of solubility was observed when in
contact
with humidity, guarantying an excellent marginal sealing. |
| |
|
|
| |
|
Action Mode:
- Inducing the formation of dentinal layer.
- Exclusive material capable to induce neo-formation of cement. |
| |
|
|
 |
|
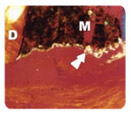
Reaction of conjunctive tissue of mices
to
tubules of Dentine obtured with MTA-Angelus. Holland et al, 2001.
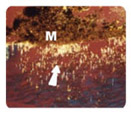
Figure 1. Please note MTA Angelus (M) inside the dentine tubule
(D).
Close to the surface of the material there is calcite granulations (arrow). Polarized light. 80 X. |
| |
|
|
 |
|
Figure 2. Note calcite granulations (arrow) inside the dentinal
tubules and the MTA-angelus (M) inside the dentine tubule.
Polarized
light. 80 X. |
| |
|
|
 |
|
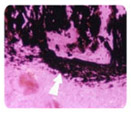
Figure 3. Note a positive pontic of hard tissue Von Kossa
(arrow)
close to the entrance of the tubule. Von Kossa 100 X. |
| |
|
|
 |
|
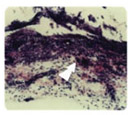
Figure 4.Ao H.E. We can note basofile areas (arrow)
corresponding to
the calcification areas and conjunctive. tissue. with a few
chronic type
inflammatory cells. H.E. 100 X. |
| |
|
|
| |
|
Previous treatment with Calcium
Hydroxide
- In the cases where a previous injury exists, with
consequent
local
inflammation, the application of HCal before the treatment
with
MTA,
permit us to have control of the severe process and
the bacterial
infection.
- MTA, as any other obturator product, only should be used after
neutralization of the local adverse reactions (infectious and
inflammatory
processes). |
| |
|
|
| |
|
Sterilization
- MTA is sterilized by gamma cobalt rays.
- The subsequent sterilization is dispensable, because the pH
of
the
product is highly alkaline (10.2), not allowing the bacterial
growth. |
| |
|
|
| |
|
Presence of heavy metals
A heavy metal control process (mainly Arsenic, Lead and Chrome)
is
performed during the production of White MTA, to keep the amount
of such
metals inside the limits permitted by the Health Ministry. |
| |
|
|
 |
|
White MTA
Packing with 1g sachets (07 applications).
Packing with 2g sachets (14 applications).
Packing with 02 sachets (02 applications).
Gray MTA
Packing with 1g sachets (07 applications).
Packing with 2g sachets (14 applications).
Packing with 02 sachets (02 applications). |
| |
|
|
| |
|
To prepare an average portion:
one SACHET
of the powder MTA-angelus + 01 drop of distilled water.
a - Release a powder portion and a drop of distilled water on
a
sterilized glass plate.
b - Mix both for 30 seconds until obtaining a perfect
homogenization of the components. The obtained
cement should
have a
sandy consistence, similar to the
amalgam, but more humid.
c - Insert the cement in the require place, using a sterile amalgam
holder or another instrument of professional preference.
d - Condense the material in the prepared dental cavity. |
| |
|
|
 |
|
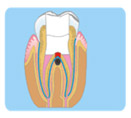
Perforation Canal, Root or Furca
a. Anesthesia, isolation.
b. Irrigation of the perforation place with sodium
hypochlorite.
c. Instrumentation, irrigation and filling of the apical
portion of the
canal up to the perforation place. |
| |
|
|
 |
|
|
| |
|
|
 |
|
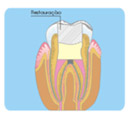
Perforation Canal, Root or Furca
e. Filling the remaining of the root canal;
f. Immediate X-rays control and after 3 to 6 months, during at
least 02
years. |
| |
|
|
 |
|
|
| |
|
|
 |
|
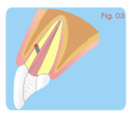
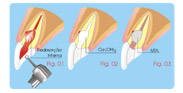
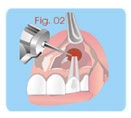
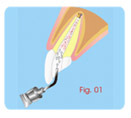
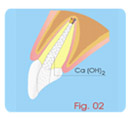
Treatment of Root Perforations for
Internal
Reabsorption ( Canal way) First Session
a - anesthesia, isolation.
b - Access to the canal and the place of the internal
reabsorption (Fig. 01).
c - irrigation with sodium hypochlorite.
d - removing pulp and granulation tissue.
e- applying calcium hydroxide curative paste [Ca(OH)2 +
distilled
water]. (Fig. 02) |
|
| |
|
|
 |
|
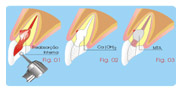
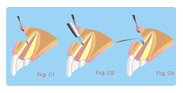
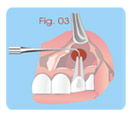
Treatment of Root Perforations for Internal
Reabsorption (Canal
way) Second Session
a- Removing of calcium hydroxide with sodium
hypochlorite.
b- Filling the apical portion of the canal.
c- Prepare White MTA and filling the place of reabsorption
with
the use
of condensers or pieces of sterile cotton
(fig.03).
d-Immediate X-rays control and after 3 to 6 months for at
least
02
years. |
|
| |
|
|
 |
|
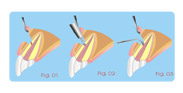
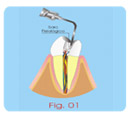
Treatment of Root Perforations (Surgical Way) The surgical way is indicated in the cases where there was
failure in
the treatment of the perforation using the technique canal way.
Surgical Technique
a- Rising the piece for locating the place of the perforation
(Fig.01).
b- Preparing the perforation with drills in order to make
easier the
condensation of the material (Fig. 02) |
|
| |
|
|
 |
|
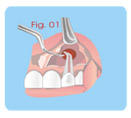
c- Controlling local bleeding.
d- Preparing MTA-Angelus and applicate in the root cavity
with
condensers (Fig.03).
e- Remotion of material excess (do not irrigate).
f- Suture and immediate X-rays control.
g- X-rays control after 3 to 6 months for at least 02 years.
H- Treatment of Root Perforations (Surgical Way). |
|
| |
|
|
 |
|
Para-endodontic Surgeries (As Back-filling Material )
Indicated in cases where the conventional endodontic treatment
failed
or in cases of impossibility to access to the root canal through
coronary
way.
Surgical Technique
a- Fragment separation, ostectomy and exhibition of radicular
apex. |
| |
|
|
 |
|
Para-endodontic Surgeries (As Back-filling Material)
b- Root resection around 2 to 3mm of the apex.
c- Preparing the retro-cavity, class I.
d- Control of the moist in the environment. |
| |
|
|
 |
|
Para-endodontic Surgeries (As Back-filling Material)
e- Preparing White MTA and application in the place with
amalgam holder
and special apical condensers.
f- Removal of excess material (do
not
irrigate).
g-Bleeding induction from the periodontal ligament and bone
tissue for
exhibiting the filling of the MTA-Angelus to the blood,
with the
purpose
of induce its hardening, this happening under
humidity presence.
h -Suture and immediate X-rays control.
i - X-rays control for at least years. |
| |
|
|
 |
|
Direct Pulp Capping
The application of White MTA on the pulp in DPC, has an
objective, the
treatment of the exposed pulp with burs, caries or fractures.
a- Anesthesia.
b- Removal of the caries.
c- Antisepsis of the cavity with sodium hypochlorite.
d- Preparing MTA-angelus.
e- Cover the place of the damage with the MTA-White.
f - Placement of the liner material and temporary restoration.
g- Post-operatory control for checking the vitality pulp. |
| |
|
|
 |
|
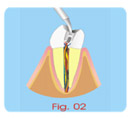
Pulpotomy and Apexogenesis
The surgical technique for both cases follows the same sequence
a- Anesthesia, absolute isolation.
b- Access to the pulp chamber, removal of the coronary pulp and
irrigation with physiologic saline solution. |
| |
|
|
 |
|
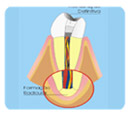
Pulpotomy and Apexogenesis
c- Bleeding control. |
| |
|
|
 |
|
Pulpotomy and Apexogenesis
h - Clinical control in relation to the symptoms, and X-rays control
each 3 months up to the root formation.
i - After the radicular formation has been completed, can be
opt for
conventional endodontic treatment or just restoration of the
coronary
cavity. |
| |
|
|
 |
|
Pulpotomy and Apexogenesis
e - Adapting the applied material with a piece of moist cotton.
f - Protecting the material with a sterile cotton on the
material.
g - Temporary restoration. |
| |
|
|
 |
|
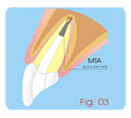
Apexification
First Session:
a- Anesthesia, absolute isolation.
b- Access to the pulp chamber, odontometry and biomechanics
of the
root canal, irrigating with sodium hypochlorite. |
| |
|
|
 |
|
Apexification
c- Placing calcium hydroxide paste with distilled water, as
intra-
root curative, for one week. |
| |
|
|
 |
|
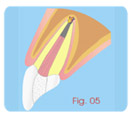
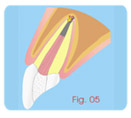
Apexification
Second Session:
a- Irrigation with sodium hypochlorite for eliminating the
calcium
hydroxide paste.
b- Drying with absorbent paper cones.
c- Preparing MTA-Angelus.
d- Obturing the canal with cement, condensing it until the apical
part of the canal using paper cones or apical condensers,
forming
an
apical cover of 3 to 4 mm. |
| |
|
|
 |
|
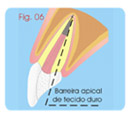
Apexification
e- Immediate X-rays control for checking the correct
obturation
canal.
f- Place moist cotton piece in the entrance of the canal.
g- Restoration of the tooth with provisory material for 24
hours. |
| |
|
|
 |
|
Apexification
Third Session:
a- Removing provisory restoration and the cotton piece.
b- Obture the remaining root canal, with gutta-percha and
conventional endodontic cement.
Important TIP: if the walls of
the
canal are very thin, its reinforcement is recommended, using
composite
resin. |
| |
|
|
 |
|
Apexification
c- Definitive restoration.
d- Clinical and X-rays control after 3 to 6 months, until confirming
the formation of the apical hard tissue. |
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
| Clinical Cases |
| |
1- Sealing ability of MTA, Super EBA, Vitremer and
amalgamas
root-end filling
materials |
| Pulpal and periradicular pathoses develop more frequently in consequence of the bacterial contaminaton of these tissues. |